Here’s my 2025 Q1 income update as a companion post to my 2025 Q1 asset allocation & performance update. Even though I don’t focus on high-dividend stocks or covered-call income strategies – I still track the income from my portfolio as an alternative metric to price performance. The total income goes up much more gradually and consistently than the number shown on brokerage statements, which helps encourage consistent investing. Here’s a related quote from Jack Bogle (source):
The true investor will do better if he forgets about the stock market and pays attention to his dividend returns and to the operating results of his companies. – Jack Bogle
Stock dividends are a portion of profits that businesses have decided to distribute directly to shareholders, as opposed to reinvesting into their business, paying back debt, or buying back shares.
They have explicitly decided that they don’t need this money to improve their business, and that it would be better to distribute it to shareholders. The dividends may suffer some short-term drops, but over the long run they have grown faster than inflation.
Here is the historical growth of the S&P 500 total dividend, which tracks roughly the largest 500 stocks in the US, updated as of 2025 Q2 (via Yardeni Research):
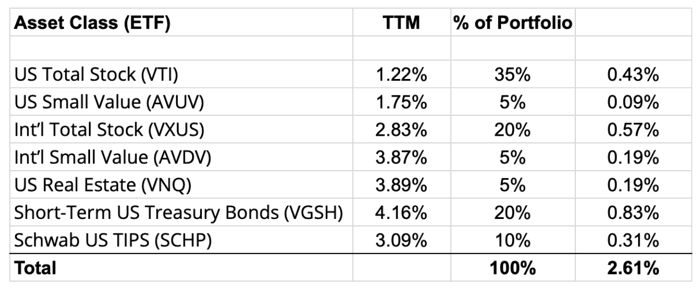
Tracking the income from my portfolio. Three of the primary income “trees” that distribute income in my portfolio are Vanguard Total US Stock ETF (VTI), Vanguard Total International Stock ETF (VXUS), and Vanguard Real Estate Index ETF (VNQ).
In the US, the dividend culture is somewhat conservative in that shareholders expect dividends to be stable and only go up. Thus the starting yield is lower, but grows more steadily with smaller cuts during hard times. Companies do buybacks as well, often because they are easier to discontinue.
Here is the updated 2010-2025 chart of the trailing 12-month (ttm) dividend per share paid by the Vanguard Total US Stock ETF (VTI) via WallStNumbers.com.
European corporate culture tends to encourage paying out a higher (sometimes even fixed) percentage of earnings as dividends, but that also means the dividends move up and down with earnings. The starting yield is currently higher but may not grow as reliably. Here is the updated 2010-2025 chart of the trailing 12-month (ttm) dividend per share paid by the Vanguard Total International Stock ETF (VXUS).
In the case of Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs), they are legally required to distribute at least 90 percent of their taxable income to shareholders as dividends. Historically, about half of the total return from REITs is from this dividend income.
Here is the updated 2005-2025 chart of the trailing 12-month (ttm) dividend per share paid by the Vanguard Real Estate Index ETF (VNQ). I extended this one out because the history was available to go beyond the 2008 Financial Crisis.
The dividend yield (dividends divided by price) also serve as a rough valuation metric. When stock prices drop, this percentage metric usually goes up – which makes me feel better in a bear market. When stock prices go up, this percentage metric usually goes down, which keeps me from getting too euphoric during a bull market.
Finally, the last income component of my portfolio comes from interest from bonds and cash.
Vanguard Short-Term Treasury ETF (VGSH) and Schwab US TIPS ETF (SCHP) are example holdings, with the actual amount varying with the prevailing interest rates, the real rates on TIPS, and the current rate of inflation.
Dividend and interest income yield. To estimate the income from my portfolio, I use the weighted “TTM” or “12-Month Yield” from Morningstar (checked 7/3/24), which is the sum of the trailing 12 months of interest and dividend payments divided by the last month’s ending share price (NAV) plus any capital gains distributed (usually zero for index funds) over the same period. My TTM portfolio yield is now roughly 2.61%.
In dividend investing circles, there is a metric called yield on cost, which is calculated by dividing the current dividend by the original purchase price. In other words, while my portfolio yield today is 2.61%, that is because the current market price is also a lot higher. The yield-on-cost based on say 10 years ago, may be on the order of 5% or so. 2.61% may not seem like a lot today, but as you watch it grow it feels very powerful.
What about the 4% rule? For big-picture purposes, I support the simple 4% or 3% rule of thumb, which equates to a target of accumulating roughly 25 to 33 times your annual expenses.
I would lean towards a 3% withdrawal rate if you want to retire young (closer to age 50) and a 4% withdrawal rate if retiring at a more traditional age (closer to 65). I don’t enjoy debating this number. It’s just a quick and dirty target to get you started, not a number sent down from the heavens! You will always have time to adjust later.
During the accumulation stage, your time is better spent focusing on earning potential via better career moves, improving your skillset, networking, and/or looking for asymmetrical (unlimited upside, limited downside) entrepreneurial opportunities where you have an ownership interest.
Our dividends and interest income are not automatically reinvested.
They are simply another “paycheck”. As with our other variable paychecks, we can choose to either spend it or invest it again to compound things more quickly. You could use this money to cut back working hours, pursue a different career path, start a new business, take a sabbatical, perform charity or volunteer work, and so on. You don’t have to wait until you hit a magic number.
Our life path is very different because of this philosophy. FIRE is Life!
Disclaimer: This story is auto-aggregated by a computer program and has not been created or edited by finopulse.
Publisher: Source link